
Contents
<aside> <img src="https://image.flaticon.com/icons/svg/1828/1828885.svg" alt="https://image.flaticon.com/icons/svg/1828/1828885.svg" width="40px" /> Golden Rice is a genetically modified version of white rice that produces Vitamin-A, which is handy in countries where people (especially children) die from Vitamin-A deficiency.
</aside>
<aside> <img src="https://image.flaticon.com/icons/svg/1828/1828885.svg" alt="https://image.flaticon.com/icons/svg/1828/1828885.svg" width="40px" /> Bt-corn is genetically altered to express the bacterial Bt toxin, which is poisonous to insect pests. In the case of corn, the pest is the European Corn Borer. (Kenya)
</aside>
Biotechnology, the use of technology to allegedly manipulate genes in organisms for the benefit of human beings.
Organisms that have had their DNA changed through some form of genetic engineering. In many cases, this results in i.e. better nutrition, longer shelf life, faster growth or even better taste (purely aesthetic).
GMOs are created in order to to produce new gene combinations that result in more favorable traits, such as crops that have:
Gene splicing has four main steps:
Genes are inserted into the plasmids of bacteria using restriction enzymes to cut the DNA strands and the enzyme ligase to ”glue” the strands back together. The bacteria then produce useful products such as human growth hormone (hGH) or insulin.
Virus with desired gene is used to tranfer the gene into a living recipient cell, where it produces more copies of the gene.
DNA is transferred through a microscopic injection into the recipient cell, where it reproduces more copies of the gene.
A microscopic, gold-coated metal ball covered with DNA is shot into plant cells, where it reproduces more copies of the gene.

All plants above are artificially selected from mustard plants. Photo: Britannica.
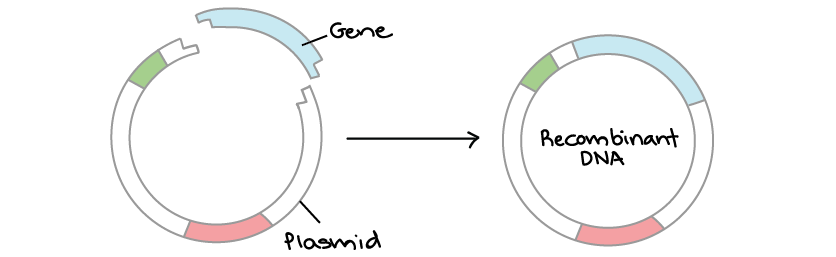
The insertion of a gene into a plasmid to produce a molecule of recombinant DNA. Photo: Khan Academy.